Page 20 - Revista Portuguesa - SPORL - Vol 48. Nº3
P. 20
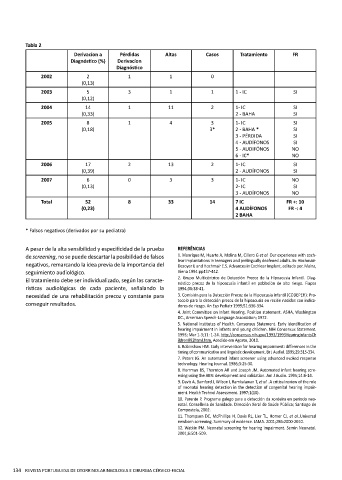
Tabla 2
Derivacíon a Pérdidas Altas Casos Tratamiento FR
Diagnóstico (%) Derivacíon
Diagnóstico
2002 2 1 1 0
(0,13)
2003 5 3 1 1 1 - IC SI
(0,12)
2004 14 1 11 2 1- IC SI
(0,33) 2 - BAHA SI
2005 8 1 4 3 1- IC SI
(0,18) 3* 2 - BAHA * SI
3 - PÉRDIDA SI
4 - AUDÍFONOS SI
5 - AUDIFÓNOS NO
6 - IC* NO
2006 17 2 13 2 1- IC SI
(0,39) 2 - AUDÍFONOS SI
2007 6 0 3 3 1- IC NO
(0,13) 2- IC SI
3 - AUDÍFONOS NO
Total 52 8 33 14 7 IC FR +: 10
(0,23) 4 AUDÍFONOS FR -: 4
2 BAHA
* Falsos negativos (derivados por su pediatra)
A pesar de la alta sensibilidad y especificidad de la prueba REFERÊNCIAS
de screening, no se puede descartar la posibilidad de falsos 1. Manrique M, Huarte A, Molina M, Cillero G et al. Our experience with coch-
negativos, remarcando la idea previa de la importancia del lear implantations in teenagers and prelingually deafened adults. In: Hochmair-
Desoyer IJ and Hochmair E.S. Advances in Cochlear Implant, editado por. Mainz,
seguimiento audiológico. Viena 1994:pp437-442.
El tratamiento debe ser individualizado, según las caracte- 2. Grupo Multicéntrico de Detección Precoz de la Hipoacusia Infantil. Diag-
nóstico precoz de la hipoacusia infantil en población de alto riesgo. Fiapas
rísticas audiológicas de cada paciente, señalando la 1994;36:38-41.
necesidad de una rehabilitación precoz y constante para 3. Comisión para la Detección Precoz de la Hipoacusia infantil (CODEPEH): Pro-
conseguir resultados. tocolo para la detección precoz de la hipoacusia en recién nacidos con indica-
dores de riesgo. An Esp Pediatr 1999;51:336-334.
4. Joint Committee on Infant Hearing. Position statement. ASHA, Washington
DC., American Speech-Language Association; 1972.
5. National Institutes of Health. Consensus Statement. Early identification of
hearing impairment in infants and young children. NIH Consensus Statement.
1993; Mar 1-3;11: 1-24. http://consensus.nih.gov/1993/1993HearingInfantsCh
ildren092html.htm. Acedido em Agosto, 2010.
6. Robinshaw HM. Early intervention for hearing impairment: differences in the
timing of communicative and linguistic development. Br J Audiol. 1995;29:315-334.
7. Peters JG. An automated infant screener using advanced evoked response
technology. Hearing Journal. 1986;3:25-30.
8. Herrman BS, Thornton AR and Joseph JM. Automated infant hearing scre-
ening using the ABR: development and validation. Am J Audio. 1995;14:6-14.
9. Davis A, Bamford J, Wilson I, Ramkalawan T, et al.. A critical review of the role
of neonatal hearing detection in the detection of congenital hearing impair-
ment. Health Technol Assessment. 1997;1(10).
10. Parente P. Programa galego para a detección da xordeira en período neo-
natal. Conselleria de Sanidade. Dirección Xeral de Saúde Pública; Santiago de
Compostela, 2002.
11. Thompson DC, McPhillips H, Davis RL, Lier TL, Homer CJ, et al..Universal
newborn screening. Summary of evidence. JAMA. 2001;286:2000-2010.
12. Watkin PM. Neonatal screening for hearing impairment. Semin Neonatol.
2001;6:501-509.
134 REVISTA PORTUGUESA DE OTORRINOLARINGOLOGIA E CIRURGIA CÉRVICO-FACIAL