Page 33 - Portuguese Journal - SPORL - Vol 61. Nº2
P. 33
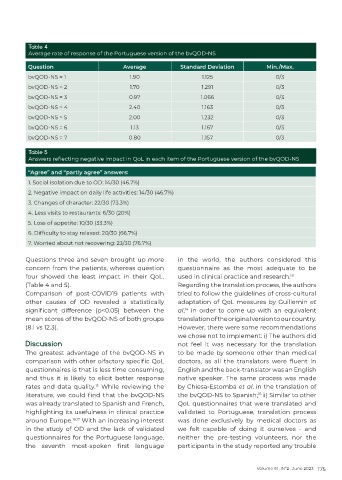
Table 4
Average rate of response of the Portuguese version of the bvQOD-NS
Question Average Standard Deviation Min./Max.
bvQOD-NS = 1 1.90 1.125 0/3
bvQOD-NS = 2 1.70 1.291 0/3
bvQOD-NS = 3 0.97 1.066 0/3
bvQOD-NS = 4 2.40 1.163 0/3
bvQOD-NS = 5 2.00 1.232 0/3
bvQOD-NS = 6 1.13 1.167 0/3
bvQOD-NS = 7 0.80 1.157 0/3
Table 5
Answers reflecting negative impact in QoL in each item of the Portuguese version of the bvQOD-NS
“Agree” and “partly agree” answers:
1. Social isolation due to OD: 14/30 (46.7%)
2. Negative impact on daily life activities: 14/30 (46.7%)
3. Changes of character: 22/30 (73.3%)
4. Less visits to restaurants: 6/30 (20%)
5. Loss of appetite: 10/30 (33.3%)
6. Difficulty to stay relaxed: 20/30 (66.7%)
7. Worried about not recovering: 23/30 (76.7%)
Questions three and seven brought up more in the world, the authors considered this
concern from the patients, whereas question questionnaire as the most adequate to be
four showed the least impact in their QoL. used in clinical practice and research. 18
(Table 4 and 5). Regarding the translation process, the authors
Comparison of post-COVID19 patients with tried to follow the guidelines of cross-cultural
other causes of OD revealed a statistically adaptation of QoL measures by Guillemin et
significant difference (p<0.05) between the al, in order to come up with an equivalent
14
mean scores of the bvQOD-NS of both groups translation of the original version to our country.
(8.1 vs 12.3). However, there were some recommendations
we chose not to implement: i) The authors did
Discussion not feel it was necessary for the translation
The greatest advantage of the bvQOD-NS in to be made by someone other than medical
comparison with other olfactory specific QoL doctors, as all the translators were fluent in
questionnaires is that is less time consuming, English and the back-translator was an English
and thus it is likely to elicit better response native speaker. The same process was made
rates and data quality. While reviewing the by Chiesa-Estomba et al. in the translation of
15
literature, we could find that the bvQOD-NS the bvQOD-NS to Spanish; ii) Similar to other
16
was already translated to Spanish and French, QoL questionnaires that were translated and
highlighting its usefulness in clinical practice validated to Portuguese, translation process
around Europe. 16,17 With an increasing interest was done exclusively by medical doctors as
in the study of OD and the lack of validated we felt capable of doing it ourselves - and
questionnaires for the Portuguese language, neither the pre-testing volunteers, nor the
the seventh most-spoken first language participants in the study reported any trouble
Volume 61 . Nº2 . June 2023 175