Page 32 - Portuguese Journal - SPORL - Vol 61. Nº2
P. 32
Statistical analysis Every patient scored below normosmia in
Statistical analysis was performed using IBM the odor threshold test with butanol, and
SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 27.0. the SnSt identification test revealed that our
Armonk, NY. The Cronbach α coefficient was population was all below the 10th percentile
used to assess the internal consistency of the according to the Portuguese normative data,
questionnaire, measuring the degree to which indicating hyposmia/anosmia. After ENT
13
each question relates to the rest. The test-retest examination and imagiological evaluation
reliability, referring to the consistency between with sinonasal computer tomography (CT)
the scores of repeated measurements from scan, patients’ etiologies of olfactory disorders
the same participant, was assessed by the were i) Chronic Rhinosinusitis (CRS) with
intraclass correlation coefficient. We used nasal polyps (CRSwNP), ii) CRS without nasal
the independent Samples t Test to compare polyps (CRSsNP), iii) post-COVID19 olfactory
groups within the population. dysfunction, or iv) post-traumatic (Table 2). No
patient was lost during the 1 month follow up.
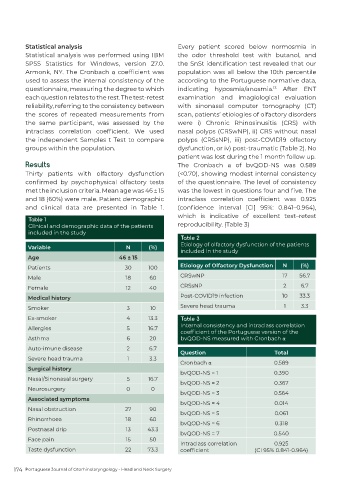
Results The Cronbach α of bvQOD-NS was 0.589
Thirty patients with olfactory dysfunction (<0.70), showing modest internal consistency
confirmed by psychophysical olfactory tests of the questionnaire. The level of consistency
met the inclusion criteria. Mean age was 46 ± 15 was the lowest in questions four and five. The
and 18 (60%) were male. Patient demographic intraclass correlation coefficient was 0.925
and clinical data are presented in Table 1. (confidence interval [CI] 95%: 0.841–0.964),
which is indicative of excellent test–retest
Table 1
Clinical and demographic data of the patients reproducibility. (Table 3)
included in the study
Table 2
Etiology of olfactory dysfunction of the patients
Variable N (%)
included in the study
Age 46 ± 15
Patients 30 100 Etiology of Olfactory Dysfunction N (%)
Male 18 60 CRSwNP 17 56.7
Female 12 40 CRSsNP 2 6.7
Medical history Post-COVID19 infection 10 33.3
Smoker 3 10 Severe head trauma 1 3.3
Ex-smoker 4 13.3 Table 3
Internal consistency and intraclass correlation
Allergies 5 16.7
coefficient of the Portuguese version of the
Asthma 6 20 bvQOD-NS measured with Cronbach α
Auto-imune disease 2 6.7
Question Total
Severe head trauma 1 3.3
Cronbach α 0.589
Surgical history
bvQOD-NS = 1 0.390
Nasal/Sinonasal surgery 5 16.7
bvQOD-NS = 2 0.367
Neurosurgery 0 0
bvQOD-NS = 3 0.564
Associated symptoms
bvQOD-NS = 4 0.014
Nasal obstruction 27 90
bvQOD-NS = 5 0.061
Rhinorrhoea 18 60
bvQOD-NS = 6 0.318
Postnasal drip 13 43.3
bvQOD-NS = 7 0.540
Face pain 15 50
Intraclass correlation 0.925
Taste dysfunction 22 73.3 coefficient (CI 95% 0.841-0.964)
174 Portuguese Journal of Otorhinolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery