Page 72 - Revista Portuguesa - SPORL - Vol 62. Nº1
P. 72
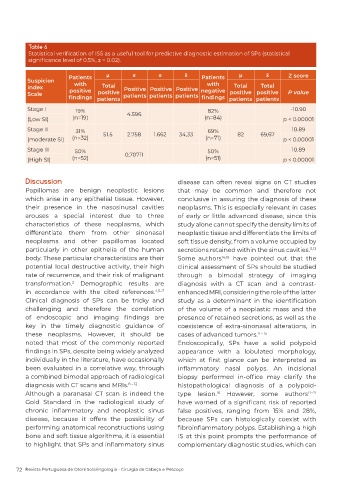
Table 6
Statistical verification of ISS as a useful tool for predictive diagnostic estimation of SPs (statistical
significance level of 0.5%, z = 0.02).
Patients μ σ σ x̄ Patients μ x̄ Z score
Suspicion with with
Index positive Total Positive Positive Positive negative Total Total
positive positive
positive
Scale findings patients patients patients patients findings patients patients P value
Stage I 19% 4.596 82% -10.90
(Low SI) (n=19) (n=84) p < 0.00001
Stage II 31% 51.5 2.758 1.662 34,33 69% 82 69,67 10.89
(moderate SI) (n=32) (n=71) p < 0.00001
Stage III 50% 50% 10.89
(High SI) (n=52) 0,70711 (n=51) p < 0.00001
Discussion disease can often reveal signs on CT studies
Papillomas are benign neoplastic lesions that may be common and therefore not
which arise in any epithelial tissue. However, conclusive in assuring the diagnosis of these
their presence in the nasosinusal cavities neoplasms. This is especially relevant in cases
arouses a special interest due to three of early or little advanced disease, since this
characteristics of these neoplasms, which study alone cannot specify the density limits of
differentiate them from other sinonasal neoplastic tissue and differentiate the limits of
neoplasms and other papillomas located soft tissue density, from a volume occupied by
particularly in other epithelia of the human secretions retained within the sinus cavities. 11,13
body. These particular characteristics are their Some authors 14,15 have pointed out that the
potential local destructive activity, their high clinical assessment of SPs should be studied
rate of recurrence, and their risk of malignant through a bimodal strategy of imaging
transformation. Demographic results are diagnosis with a CT scan and a contrast-
2
in accordance with the cited references. 4,5–7 enhanced MRI, considering the role of the latter
Clinical diagnosis of SPs can be tricky and study as a determinant in the identification
challenging and therefore the correlation of the volume of a neoplastic mass and the
of endoscopic and imaging findings are presence of retained secretions, as well as the
key in the timely diagnostic guidance of coexistence of extra-sinonasal alterations, in
these neoplasms. However, it should be cases of advanced tumors. 11 – 15
noted that most of the commonly reported Endoscopically, SPs have a solid polypoid
findings in SPs, despite being widely analyzed appearance with a lobulated morphology,
individually in the literature, have occasionally which at first glance can be interpreted as
been evaluated in a correlative way, through inflammatory nasal polyps. An incisional
a combined bimodal approach of radiological biopsy performed in-office may clarify the
diagnosis with CT scans and MRIs. 8 – 12 histopathological diagnosis of a polypoid-
Although a paranasal CT scan is indeed the type lesion. However, some authors 17–21
16
Gold Standard in the radiological study of have warned of a significant risk of reported
chronic inflammatory and neoplastic sinus false positives, ranging from 15% and 28%,
disease, because it offers the possibility of because SPs can histologically coexist with
performing anatomical reconstructions using fibroinflammatory polyps. Establishing a high
bone and soft tissue algorithms, it is essential IS at this point prompts the performance of
to highlight that SPs and inflammatory sinus complementary diagnostic studies, which can
72 Revista Portuguesa de Otorrinolaringologia - Cirurgia de Cabeça e Pescoço