Page 95 - Portuguese Journal - SPORL - Vol 61. Nº2
P. 95
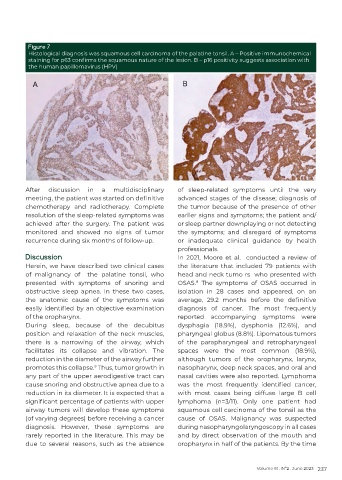
Figure 7
Histological diagnosis was squamous cell carcinoma of the palatine tonsil. A – Positive immunochemical
staining for p63 confirms the squamous nature of the lesion. B – p16 positivity suggests association with
the human papillomavirus (HPV)
After discussion in a multidisciplinary of sleep-related symptoms until the very
meeting, the patient was started on definitive advanced stages of the disease; diagnosis of
chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Complete the tumor because of the presence of other
resolution of the sleep-related symptoms was earlier signs and symptoms; the patient and/
achieved after the surgery. The patient was or sleep partner downplaying or not detecting
monitored and showed no signs of tumor the symptoms; and disregard of symptoms
recurrence during six months of follow-up. or inadequate clinical guidance by health
professionals.
Discussion In 2021, Moore et al. conducted a review of
Herein, we have described two clinical cases the literature that included 79 patients with
of malignancy of the palatine tonsil, who head and neck tumo rs who presented with
presented with symptoms of snoring and OSAS. The symptoms of OSAS occurred in
8
obstructive sleep apnea. In these two cases, isolation in 28 cases and appeared, on an
the anatomic cause of the symptoms was average, 29.2 months before the definitive
easily identified by an objective examination diagnosis of cancer. The most frequently
of the oropharynx. reported accompanying symptoms were
During sleep, because of the decubitus dysphagia (18.9%), dysphonia (12.6%), and
position and relaxation of the neck muscles, pharyngeal globus (8.8%). Lipomatous tumors
there is a narrowing of the airway, which of the parapharyngeal and retropharyngeal
facilitates its collapse and vibration. The spaces were the most common (18.9%),
reduction in the diameter of the airway further although tumors of the oropharynx, larynx,
promotes this collapse. Thus, tumor growth in nasopharynx, deep neck spaces, and oral and
9
any part of the upper aerodigestive tract can nasal cavities were also reported. Lymphoma
cause snoring and obstructive apnea due to a was the most frequently identified cancer,
reduction in its diameter. It is expected that a with most cases being diffuse large B cell
significant percentage of patients with upper lymphoma (n=3/11). Only one patient had
airway tumors will develop these symptoms squamous cell carcinoma of the tonsil as the
(of varying degrees) before receiving a cancer cause of OSAS. Malignancy was suspected
diagnosis. However, these symptoms are during nasopharyngolaryngoscopy in all cases
rarely reported in the literature. This may be and by direct observation of the mouth and
due to several reasons, such as the absence oropharynx in half of the patients. By the time
Volume 61 . Nº2 . June 2023 237