Page 94 - Portuguese Journal - SPORL - Vol 61. Nº2
P. 94
Clinical case 2: apparent extension to the anterior and
A 67 year-old man attended the Snoring and posterior pillars or the glossotonsillar sulcus.
Sleep Apnea clinic with complaints of snoring, Nasopharyngolaryngoscopy showed a
episodes of sleep apnea, and nasal obstruction reduction in the velpharyngeal space because
for the last two months, which had worsened of the enlarged right tonsil and excluded other
rapidly in the three weeks before the visit. lesions at the level of the upper aerodigestive
The relevant clinical history included tract.
smoking (60 pack-years). On objective Cervical CT confirmed the presence of a
physical examination, he had a BMI of 26.5 neoformation at the level of the right tonsil
kg/m and marked tonsil asymmetry, with with a transverse diameter of 35 mm and
2
an enlarged right palatine tonsil due to an involvement of the tonsillar pillars was not
infiltrative lesion with ulcerated areas, without excluded. There was no apparent extension
to the nasopharynx or the masticator,
parapharyngeal, and carotid spaces. There
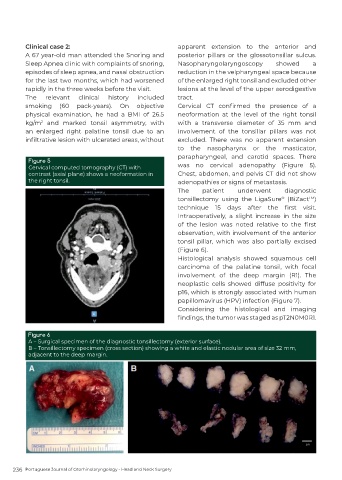
Figure 5
Cervical computed tomography (CT) with was no cervical adenopathy (Figure 5).
contrast (axial plane) shows a neoformation in Chest, abdomen, and pelvis CT did not show
the right tonsil. adenopathies or signs of metastasis.
The patient underwent diagnostic
tonsillectomy using the LigaSure (BiZact )
TM
®
technique 15 days after the first visit.
Intraoperatively, a slight increase in the size
of the lesion was noted relative to the first
observation, with involvement of the anterior
tonsil pillar, which was also partially excised
(Figure 6).
Histological analysis showed squamous cell
carcinoma of the palatine tonsil, with focal
involvement of the deep margin (R1). The
neoplastic cells showed diffuse positivity for
p16, which is strongly associated with human
papillomavirus (HPV) infection (Figure 7).
Considering the histological and imaging
findings, the tumor was staged as pT2N0M0R1.
Figure 6
A – Surgical specimen of the diagnostic tonsillectomy (exterior surface).
B – Tonsillectomy specimen (cross section) showing a white and elastic nodular area of size 32 mm,
adjacent to the deep margin.
236 Portuguese Journal of Otorhinolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery