Page 40 - Portuguese Journal - SPORL - Vol 61. Nº2
P. 40
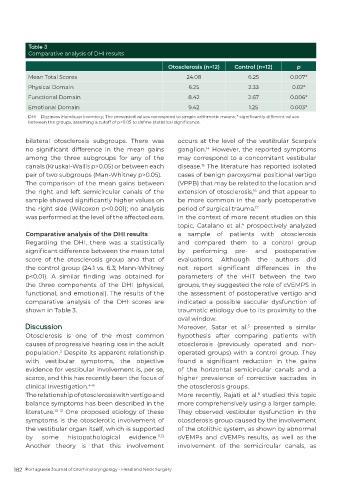
Table 3
Comparative analysis of DHI results
Otosclerosis (n=12) Control (n=12) p
Mean Total Scores 24.08 6.25 0.007*
Physical Domain 6.25 2.33 0.02*
Functional Domain 8.42 2.67 0.006*
Emotional Domain 9.42 1.25 0.003*
DHI – Dizziness Handicap Inventory; The presented values correspond to simple arithmetic means; * significantly different values
between the groups, assuming a cutoff of p<0.05 to define statistical significance.
bilateral otosclerosis subgroups. There was occurs at the level of the vestibular Scarpa’s
no significant difference in the mean gains ganglion. However, the reported symptoms
14
among the three subgroups for any of the may correspond to a concomitant vestibular
canals (Kruskal-Wallis p>0.05) or between each disease. The literature has reported isolated
15
pair of two subgroups (Man-Whitney p>0.05). cases of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo
The comparison of the mean gains between (VPPB) that may be related to the location and
the right and left semicircular canals of the extension of otosclerosis, and that appear to
16
sample showed significantly higher values on be more common in the early postoperative
the right side (Wilcoxon p<0.001); no analysis period of surgical trauma.
17
was performed at the level of the affected ears. In the context of more recent studies on this
topic, Catalano et al. prospectively analyzed
4
Comparative analysis of the DHI results a sample of patients with otosclerosis
Regarding the DHI, there was a statistically and compared them to a control group
significant difference between the mean total by performing pre- and postoperative
score of the otosclerosis group and that of evaluations. Although the authors did
the control group (24.1 vs. 6.3; Mann-Whitney not report significant differences in the
p<0.01). A similar finding was obtained for parameters of the vHIT between the two
the three components of the DHI (physical, groups, they suggested the role of cVEMPS in
functional, and emotional). The results of the the assessment of postoperative vertigo and
comparative analysis of the DHI scores are indicated a possible saccular dysfunction of
shown in Table 3. traumatic etiology due to its proximity to the
oval window.
Discussion Moreover, Satar et al. presented a similar
5
Otosclerosis is one of the most common hypothesis after comparing patients with
causes of progressive hearing loss in the adult otosclerosis (previously operated and non-
population. Despite its apparent relationship operated groups) with a control group. They
2
with vestibular symptoms, the objective found a significant reduction in the gains
evidence for vestibular involvement is, per se, of the horizontal semicircular canals and a
scarce, and this has recently been the focus of higher prevalence of corrective saccades in
clinical investigation. 4–6 the otosclerosis groups.
The relationship of otosclerosis with vertigo and More recently, Rajati et al. studied this topic
6
balance symptoms has been described in the more comprehensively using a larger sample.
literature. 10–12 One proposed etiology of these They observed vestibular dysfunction in the
symptoms is the otosclerotic involvement of otosclerosis group caused by the involvement
the vestibular organ itself, which is supported of the otolithic system, as shown by abnormal
by some histopathological evidence. 11,13 oVEMPs and cVEMPs results, as well as the
Another theory is that this involvement involvement of the semicircular canals, as
182 Portuguese Journal of Otorhinolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery