Page 80 - Revista Portuguesa - SPORL - Vol 62. Nº1
P. 80
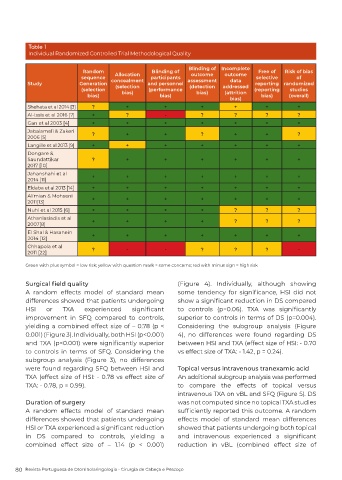
Table 1
Individual Randomized Controlled Trial Methodological Quality
Blinding of Incomplete
Random Blinding of Free of Risk of bias
sequence Allocation participants outcome outcome selective of
data
Study Generation concealment and personnel assessment addressed reporting randomized
(selection
(detection
(selection bias) (performance bias) (attrition (reporting studies
bias) bias) bias) (overall)
bias)
Shehata et al 2014 [3] ? + + + + + +
Al-Issis et al 2016 [7] + ? - ? ? ? ?
Gan et al 2003 [4] + + + + + + +
Jabalameli & Zakeri ? + + ? + + ?
2006 [5]
Langille et al 2013 [9] + + + + + + +
Dongare &
Saundattikar ? + + + + + +
2017 [10]
Jahanshahi et al + + + + + + +
2014 [11]
Eldaba et al 2013 [14] + + + + + + +
Alimian & Mohseni + + + + + + +
2011[13]
Nuhi et al 2015 [6] + + + + ? ? ?
Athaniasiadis et al + + + + ? ? ?
2007[8]
El Shal & Hasanein + + + + + + +
2014 [12]
Chhapola et al ? - - ? ? ? -
2011 [22]
Green with plus symbol = low risk; yellow with question mark = some concerns; red with minus sign = high risk
Surgical field quality (Figure 4). Individually, although showing
A random effects model of standard mean some tendency for significance, HSI did not
differences showed that patients undergoing show a significant reduction in DS compared
HSI or TXA experienced significant to controls (p=0.06). TXA was significantly
improvement in SFQ compared to controls, superior to controls in terms of DS (p=0.004).
yielding a combined effect size of – 0.78 (p < Considering the subgroup analysis (Figure
0.001) (Figure 3). Individually, both HSI (p<0.001) 4), no differences were found regarding DS
and TXA (p<0.001) were significantly superior between HSI and TXA (effect size of HSI: - 0.70
to controls in terms of SFQ. Considering the vs effect size of TXA: - 1.42, p = 0.24).
subgroup analysis (Figure 3), no differences
were found regarding SFQ between HSI and Topical versus intravenous tranexamic acid
TXA (effect size of HSI: - 0.78 vs effect size of An additional subgroup analysis was performed
TXA: - 0.78, p = 0.99). to compare the effects of topical versus
intravenous TXA on vBL and SFQ (Figure 5). DS
Duration of surgery was not computed since no topical TXA studies
A random effects model of standard mean sufficiently reported this outcome. A random
differences showed that patients undergoing effects model of standard mean differences
HSI or TXA experienced a significant reduction showed that patients undergoing both topical
in DS compared to controls, yielding a and intravenous experienced a significant
combined effect size of – 1.14 (p < 0.001) reduction in vBL (combined effect size of
80 Revista Portuguesa de Otorrinolaringologia - Cirurgia de Cabeça e Pescoço