Page 79 - Revista Portuguesa - SPORL - Vol 62. Nº1
P. 79
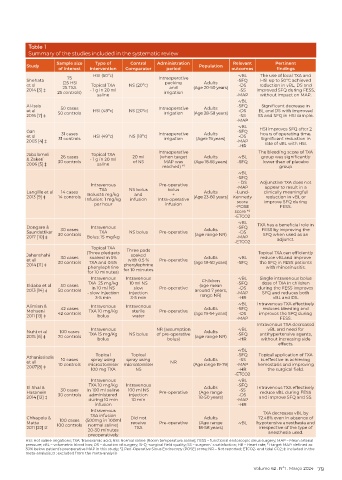
Table 1
Summary of the studies included in the systematic review
Sample size Type of Control Administration Relevant Pertinent
Study Population
of interest intervention Comparator period outcomes findings
HSI (50ºc) -vBL The use of local TXA and
75 Intraoperative
Shehata (25 HSI packing Adults -SFQ HSI up to 50°C achieved
et al 25 TXA Topical TXA NS (20ºc) and (Age 20-50 years) -DS reduction in vBL, DS and
2014 [3] ‡ - 1 g in 20 ml -SS improved SFQ during FESS,
25 controls) irrigation
saline -MAP without impact on MAP.
-vBL
Al-Issis 50 cases Intraoperative Adults -SFQ Significant decrease in
et al 50 controls HSI (48ºc) NS (20ºc) irrigation (Age 28-58 years) -DS BL and DS with improved
2016 [7] ‡ -SS SS and SFQ in HSI sample.
-MAP
-vBL
Gan 31 cases Intraoperative Adults -SFQ HSI improves SFQ after 2
hours of operating time.
et al 31 controls HSI (49ºc) NS (18ºc) irrigation (Age≥ 19 years) -DS Significant reduction in
2003 [4] ‡ -MAP rate of vBL with HSI.
-HR
Jabalameli 26 cases Topical TXA 20 ml Intraoperative Adults -vBL The bleeding score of TXA
group was significantly
(when target
& Zakeri 30 controls - 1 g in 20 ml of NS MAP was (Age 18-55 years) -SFQ lower than of placebo
2006 [5] ‡ saline reached) * 1 group
-vBL
-SFQ
- DS Adjunctive TXA does not
Intravenous Pre-operative -MAP appear to result in a
TXA NS bolus bolus
Langille et al 14 cases Bolus:15 mg/kg and + Adults -Lund- clinically meaningful
2013 [9] ‡ 14 controls (Age 23-80 years) Kennedy reduction in vBL or
Infusion: 1 mg/kg infusion Intra-operative score improve SFQ during
per hour infusion
-POSE FESS.
score * 2
-ETCO2
-vBL
Dongare & 30 cases Intravenous Adults -SFQ TXA has a beneficial role in
FESS by improving the
Saundattikar 30 controls TXA NS bolus Pre-operative (age range NR) -DS SFQ when used as an
2017 [10] ‡ Bolus: 15 mg/kg -MAP adjunct.
-ETCO2
Topical TXA
(Three pledgets Three pads Topical TXA can efficiently
Jahanshahi 30 cases soaked in 5% soaked Adults -vBL reduce vBLand improve
et al 30 controls TXA and 0.5% with 0.5 % Pre-operative (age 18-60 years) -SFQ the SFQ in FESS patients
2014 [11] ‡ phenylephrine
phenylephrine with rhinosinusitis.
for 10 minutes) for 10 minutes
Intravenous Intravenous Children -vBL Single intravenous bolus
dose of TXA in children
Eldaba et al 50 cases TXA 25 mg/kg 10 ml NS Pre-operative (age mean -SFQ during the FESS improves
in 10 ml NS
slow
-DS
2013 [14] ‡ 50 controls - slow injection injection around 7 years, -MAP SFQ and reduces both
3-5 min 3-5 min range NR) -HR vBL and DS.
-vBL
Alimian & 42 cases Intravenous Intravenous Adults -SFQ Intravenous TXA effectively
reduces bleeding and
Mohseni 42 controls TXA 10 mg/Kg sterile Pre-operative (age 19-64 years) -DS improves the SFQ during
2011 [13] ‡ bolus water -MAP FESS.
Intravenous TXA decreased
Intravenous NR (assumption -vBL vBL and need for
Nuhi et al 100 cases TXA 15 mg/Kg NS bolus of pre-operative Adults -SFQ antihypertensive agents,
2015 [6] ‡ 70 controls (age range NR)
bolus bolus) -HR without increasing side
effects.
-vBL
Topical Topical -SFQ Topical application of TXA
Athaniasiadis 10 cases spray using spray using Adults -SS is effective in achieving
et al 10 controls microatomiser microatomiser NR (Age range 19-79) -MAP hemostasis and improving
2007[8] ‡
100 mg TXA NS -HR the surgical field.
-ETCO2
Intravenous -vBL
TXA 10 mg/Kg Intravenous -SFQ
El Shal & 30 cases in 100 ml saline 100 ml NS Adults -SS Intravenous TXA effectively
Hasanein 30 controls administered injection Pre-operative (Age range -DS reduce vBL during FESS
2014 [12] ‡ 18-50 years) and improve SFQ and SS.
during 10 min 10 min -MAP
infusion -HR
Intravenous TXA decreases vBL by
TXA infusion
Chhapola & 100 cases (500mg in 100ml Did not Adults 72.48% even in absence of
Matta 100 controls normal saline) receive Pre-operative (Age range -vBL hypotensive anesthesia and
2011 [22] ¤ TXA 18-58 years) irrespective of the type of
20-30 minutes anesthesia used.
preoperatively
HSI: Hot saline irrigations; TXA: Tranexamic acid; NSI: Normal saline (Room temperature saline); FESS – functional endoscopic sinus surgery; MAP – Mean arterial
pressure; vBL – volumetric blood loss; DS – duration of surgery; SFQ -surgical field quality; SS – surgeon´s satisfaction; HR – Heart rate; *1 target MAP: defined as
30% below patient’s preoperative MAP in this study; *2 Peri-Operative Sinus Endoscopy (POSE) score; NR – Not reported; ETCO2- end tidal CO2; ‡: included in the
meta-analysis; ¤ : excluded from the meta-analysis
Volume 62 . Nº1 . Março 2024 79